In today's digital age, mobile applications (apps) have become essential tools for businesses and consumers alike. App development involves creating software applications designed to run on mobile devices and other platforms. This guide explores the intricacies of App Development Company, its working processes, use cases, and everything else you need to know to understand and leverage this powerful technology.
What is App Development?
App development is the process of designing, creating, and deploying software applications that run on mobile devices, tablets, smartwatches, and other platforms. It involves multiple stages, including planning, designing, coding, testing, and maintenance, ensuring the final product meets user needs and performs efficiently.
Types of Apps
-
Native Apps
- Description: Built specifically for a particular platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific programming languages (Swift or Objective-C for iOS, Java or Kotlin for Android).
- Pros: High performance, better user experience, access to device features.
- Cons: Higher development costs, longer development time.
-
Web Apps
- Description: Responsive websites that adapt to the user's device. They run in a web browser and are built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Pros: Cost-effective, easy to update, cross-platform compatibility.
- Cons: Limited access to device features, lower performance compared to native apps.
-
Hybrid Apps
- Description: Combine elements of both native and web apps. Built using web technologies but wrapped in a native shell to run on mobile devices.
- Pros: Faster development, cost-effective, cross-platform.
- Cons: Potentially lower performance and user experience compared to native apps.
-
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
- Description: Web applications that offer an app-like experience in a web browser. Built using modern web capabilities.
- Pros: No need for app store distribution, offline functionality, cross-platform.
- Cons: Limited access to device hardware, less visibility in app stores.
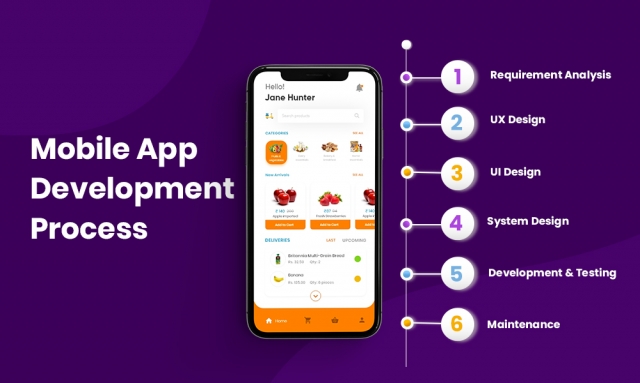
The App Development Process
-
Ideation and Planning
- Conceptualization: Define the app's purpose, target audience, and core features.
- Market Research: Analyze competitors, identify market needs, and validate the app idea.
- Technical Feasibility: Assess the technical requirements and feasibility of the app.
-
Design
- Wireframing: Create wireframes to outline the app's structure and flow.
- User Interface (UI) Design: Design the visual elements of the app, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Focus on optimizing the app's usability and interaction design.
-
Development
- Front-End Development: Implement the app's user interface using relevant technologies.
- Back-End Development: Develop the server-side logic, database management, and APIs to support the app's functionality.
- Integration: Integrate front-end and back-end components to ensure seamless communication.
-
Testing
- Functional Testing: Verify that all features work as intended.
- Performance Testing: Ensure the app performs well under various conditions.
- Usability Testing: Gather feedback from real users to improve the app's user experience.
- Security Testing: Identify and fix vulnerabilities to protect user data.
-
Deployment
- App Store Submission: Submit the app to app stores (Apple App Store, Google Play Store) and adhere to their guidelines.
- Deployment to Web: For web apps and PWAs, deploy the app to a web server and configure the necessary settings.
-
Maintenance and Updates
- Bug Fixes: Address issues reported by users.
- Feature Enhancements: Continuously improve the app by adding new features and functionalities.
- Regular Updates: Ensure the app stays compatible with the latest OS versions and devices.
Use Cases of App Development
-
E-Commerce
- Examples: Amazon, eBay, Shopify.
- Benefits: Enhance customer engagement, provide personalized shopping experiences, increase sales.
-
Social Networking
- Examples: Facebook, Instagram, Twitter.
- Benefits: Connect users, facilitate communication, enable content sharing.
-
Health and Fitness
- Examples: MyFitnessPal, Fitbit, Headspace.
- Benefits: Track health metrics, provide workout routines, offer mental wellness support.
-
Finance and Banking
- Examples: PayPal, Venmo, Mint.
- Benefits: Enable mobile payments, manage finances, provide secure transactions.
-
Education
- Examples: Duolingo, Coursera, Khan Academy.
- Benefits: Offer online courses, facilitate remote learning, provide educational resources.
-
Entertainment
- Examples: Netflix, Spotify, TikTok.
- Benefits: Stream media content, provide interactive experiences, offer personalized recommendations.
-
Travel and Hospitality
- Examples: Airbnb, Uber, Booking.com.
- Benefits: Simplify booking processes, enhance travel experiences, provide real-time information.
Benefits of App Development
-
Enhanced User Engagement
- Apps offer personalized experiences, push notifications, and real-time updates, keeping users engaged.
-
Increased Brand Visibility
- A mobile app can significantly boost brand presence and recognition, reaching a wider audience.
-
Direct Marketing Channel
- Apps provide a direct channel to communicate with users, offering promotions, updates, and customer support.
-
Revenue Generation
- Apps can generate revenue through various monetization strategies, including in-app purchases, subscriptions, and ads.
-
Improved Customer Loyalty
- Offering a seamless and enjoyable app experience fosters customer loyalty and encourages repeat usage.
-
Data Collection and Analysis
- Apps provide valuable insights into user behavior, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their offerings.
Key Considerations for App Development
-
Target Audience
- Understand your target audience's preferences, behaviors, and needs to design an app that resonates with them.
-
Platform Selection
- Choose the right platform (iOS, Android, web) based on your target audience and business objectives.
-
Security
- Implement robust security measures to protect user data and ensure compliance with regulations.
-
User Experience
- Prioritize a smooth, intuitive, and enjoyable user experience to maximize user satisfaction and retention.
-
Performance
- Ensure the app performs well under various conditions, including high traffic and limited connectivity.
-
Scalability
- Design the app to scale with your business growth, accommodating increasing user numbers and expanding features.
Conclusion
App development is a multifaceted process that transforms innovative ideas into functional and engaging software applications. By understanding the types of apps, development processes, use cases, and benefits, businesses can effectively leverage app development to enhance user engagement, drive growth, and achieve their strategic goals. Whether you're developing an e-commerce platform, a social networking app, or a fitness tracker, a well-executed app can provide immense value to both your business and your users.